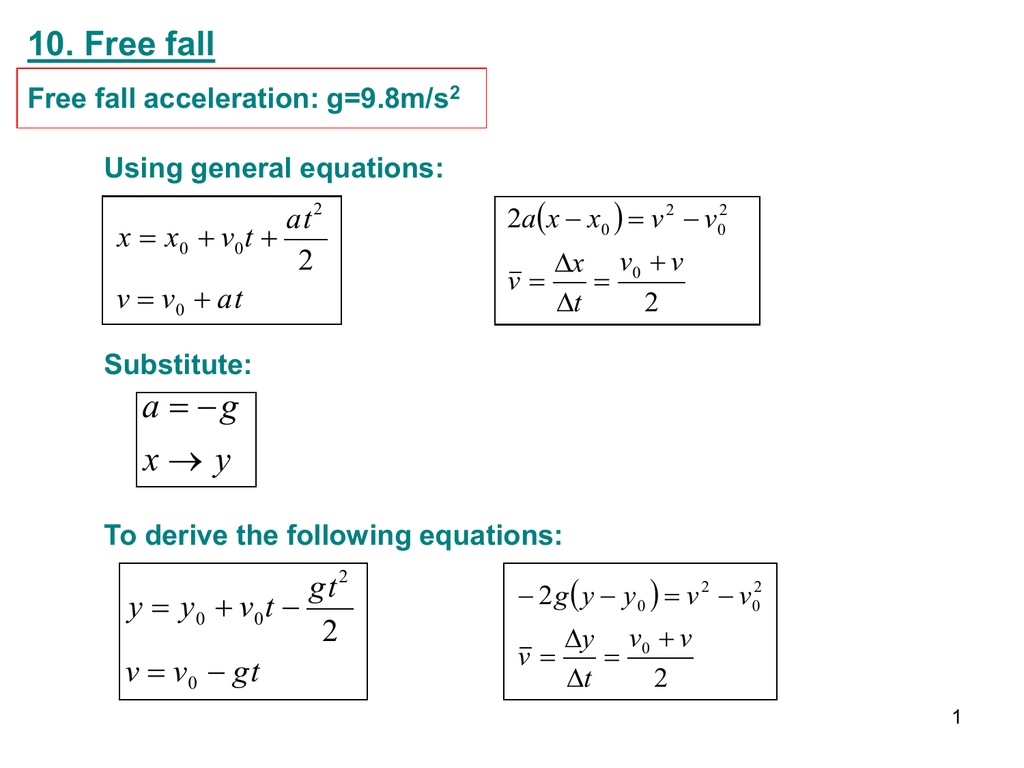
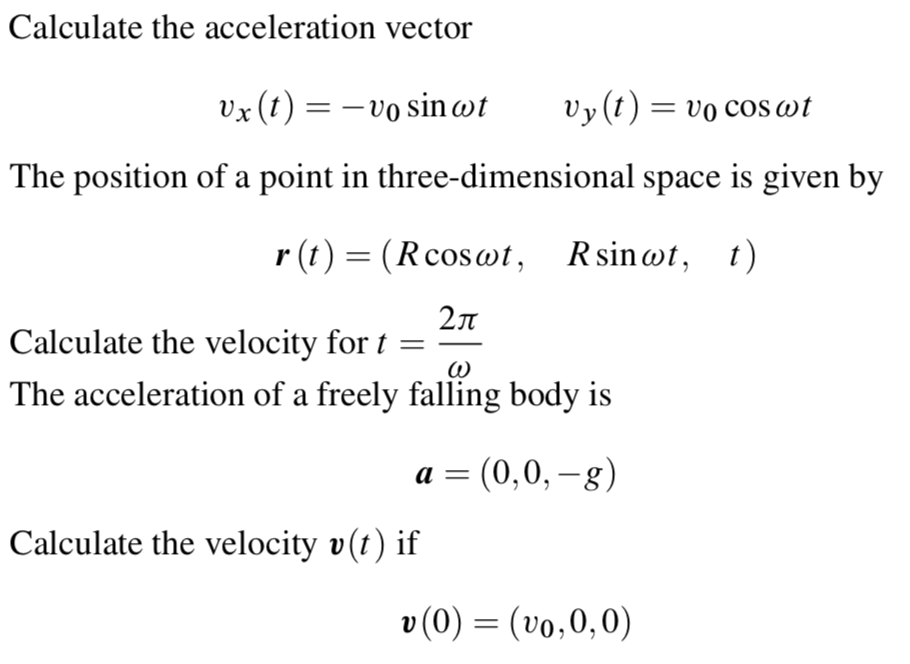
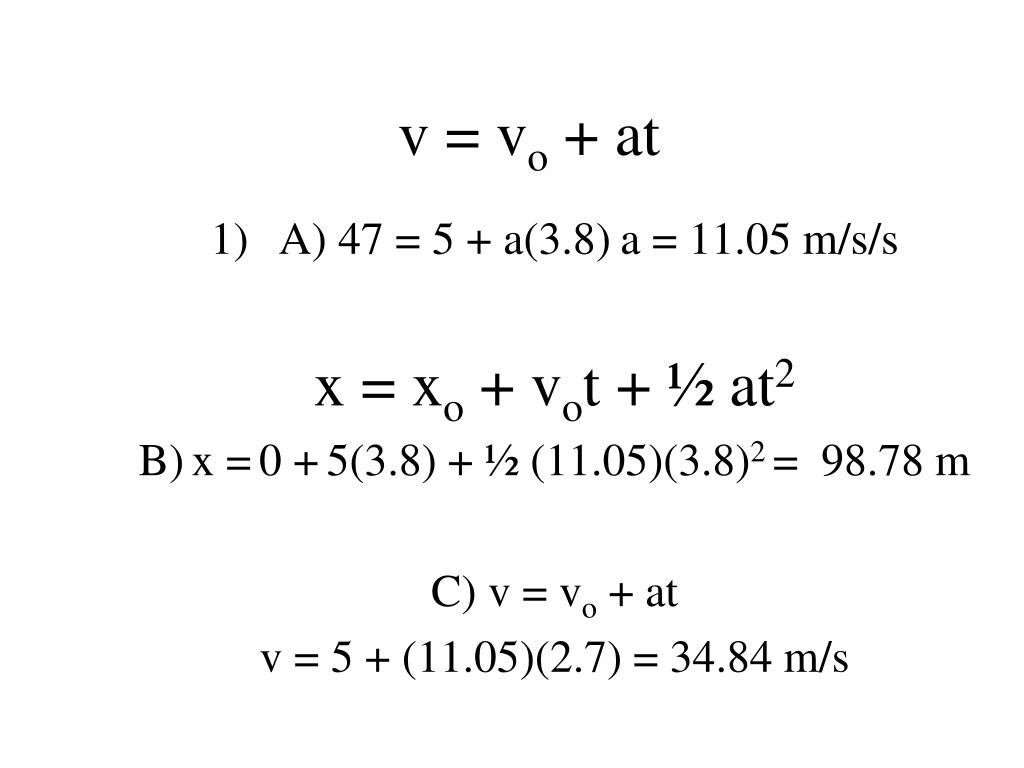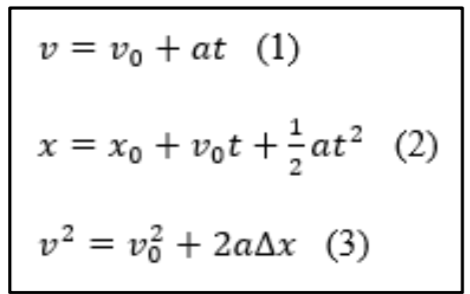How to calculate x(t)? A particle is given an impulse which imparts to it a velocity v0. It then undergoes acceleration given by a=-bv where b is constant and v is velocity.
How is the definition of acceleration equation (v(avg) =v0+a*t) a rearrangement of the equation for acceleration (a(avg) =Δv/Δt)? - Quora
One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a process P=P0/(2+V0/V),(where P0 and V0 are constant).Change in temperature of the gas when volume is changed from V =V0 to V =3V0 is

A rock is thrown from the roof of a building with a velocity v0 at an angle of theta from the horizontal. The building has a height h. You can ignore air
Volume of a sphere, V is increasing at a constant rate At the moment when volume of is V0, the rate of change of radius is
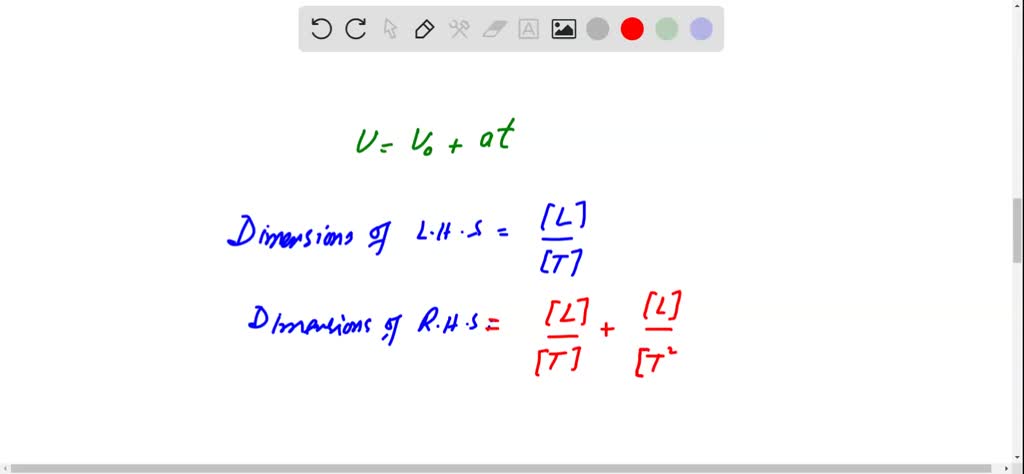
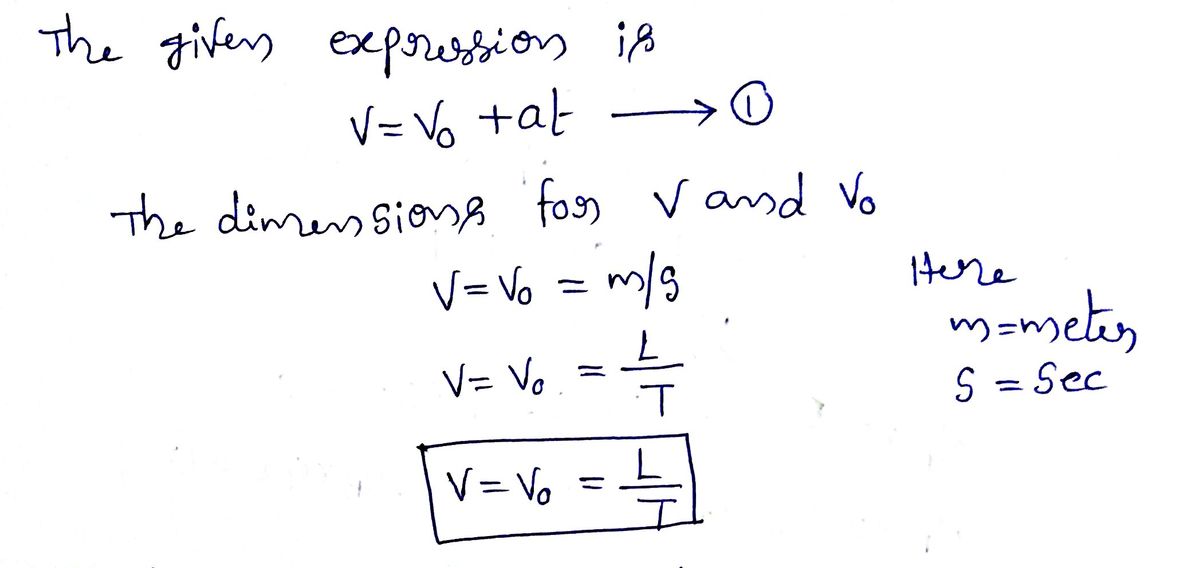
SOLVED:Show that the equation v=v0+a t is dimensionally consistent. Note that v and v0 are velocities and that a is an acceleration.

The velocity of a particle is v = v0 + gt + ft^2 . If its position is x = 0 at t = 0, then its displacement after unit time (t = 1) is: